Interference Detection and Active Avoidance
4 minute read
QOS Ensurance Architecture
QOS ensurance’s architecture is shown as below. It contains three modules.
- state collector: collect metrics periodically
- anomaly analyzer: analyze the node triggered anomaly used collected metrics
- action executor: execute avoidance actions, include disable scheduling, throttle and eviction.
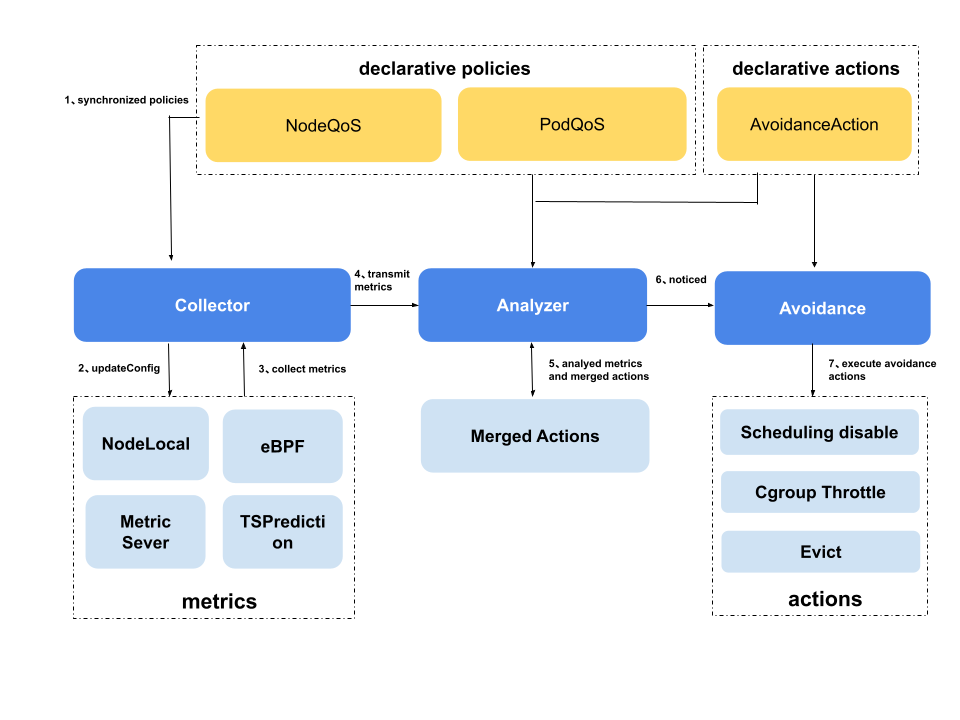
The main process:
- State collector synchronizes policies from kube-apiserver.
- If the policies are changed, the state collector updates the collectors.
- State collector collects metrics periodically.
- State collector transmits metrics to anomaly analyzer.
- Anomaly analyzer ranges all rules to analyze the avoidance threshold or the restored threshold reached.
- Anomaly analyzer merges the analyzed results and notices the avoidance actions.
- Action executor executes actions based on the analyzed results.
Interference Detection and Active Avoidance
Related CR
AvoidanceAction mainly defines the operations that need to be performed after interference is detected, including several operations such as Disable Scheduling, throttle, and eviction, and defines some related parameters.
NodeQOS mainly defines the metrics collection method and parameters, the related parameters of the watermark, and the associated avoidance operation when metrics are abnormal. At the same time, the above content is associated to the specified nodes through a series of selectors.
PodQOS defines the AvoidanceAction that a specified pod can be executed, and is usually paired with NodeQOS to limit the scope of execution actions from the dimensions of nodes and pods. The selector supported by PodQOS includes label selector, and also supports filtering of specific QOSClass (“BestEffort”, “Guaranteed”, etc.), specific Priority, and specific Namespace of pods, above selectors are associated with each other in the manner of “AND”.
Disable Scheduling
The following AvoidanceAction and NodeQOS can be defined. As a result, when the node CPU usage triggers the threshold, disable schedule action for the node will be executed.
The sample YAML looks like below:
apiVersion: ensurance.crane.io/v1alpha1
kind: AvoidanceAction
metadata:
labels:
app: system
name: disablescheduling
spec:
description: disable schedule new pods to the node
coolDownSeconds: 300 # The minimum wait time of the node from scheduling disable status to normal status
apiVersion: ensurance.crane.io/v1alpha1
kind: NodeQOS
metadata:
name: "watermark1"
spec:
nodeQualityProbe:
timeoutSeconds: 10
nodeLocalGet:
localCacheTTLSeconds: 60
rules:
- name: "cpu-usage"
avoidanceThreshold: 2 #(1)
restoreThreshold: 2 #(2)
actionName: "disablescheduling" #(3)
strategy: "None" #(4)
metricRule:
name: "cpu_total_usage" #(5)
value: 4000 #(6)
- We consider the rule is triggered, when the threshold reached continued so many times
- We consider the rule is restored, when the threshold not reached continued so many times
- Name of AvoidanceAction which be associated
- Strategy for the action, you can set it “Preview” to not perform actually
- Name of metric
- Threshold of metric
apiVersion: ensurance.crane.io/v1alpha1
kind: PodQOS
metadata:
name: all-elastic-pods
spec:
allowedActions:
- disablescheduling
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
preemptible_job: "true"
- The action allowed to be executed by the pod associated with the PodQOS is eviction
- Associate pods with preemptible_job: “true” via label selector
Please check the video to learn more about the scheduling disable actions.
Throttle
The following AvoidanceAction and NodeQOS can be defined. As a result, when the node CPU usage triggers the threshold, throttle action for the node will be executed.
The sample YAML looks like below:
apiVersion: ensurance.crane.io/v1alpha1
kind: AvoidanceAction
metadata:
name: throttle
labels:
app: system
spec:
coolDownSeconds: 300
throttle:
cpuThrottle:
minCPURatio: 10 #(1)
stepCPURatio: 10 #(2)
description: "throttle low priority pods"
- The minimal ratio of the CPU quota, if the pod is throttled lower than this ratio, it will be set to this.
- The step for throttle action. It will reduce this percentage of CPU quota in each avoidance triggered.It will increase this percentage of CPU quota in each restored.
apiVersion: ensurance.crane.io/v1alpha1
kind: NodeQOS
metadata:
name: "watermark2"
spec:
nodeQualityProbe:
timeoutSeconds: 10
nodeLocalGet:
localCacheTTLSeconds: 60
rules:
- name: "cpu-usage"
avoidanceThreshold: 2
restoredThreshold: 2
actionName: "throttle"
strategy: "None"
metricRule:
name: "cpu_total_usage"
value: 6000
apiVersion: ensurance.crane.io/v1alpha1
kind: PodQOS
metadata:
name: all-be-pods
spec:
allowedActions:
- throttle
scopeSelector:
matchExpressions:
- operator: In
scopeName: QOSClass
values:
- BestEffort
Eviction
The following YAML is another case, low priority pods on the node will be evicted, when the node CPU usage trigger the threshold.
apiVersion: ensurance.crane.io/v1alpha1
kind: AvoidanceAction
metadata:
name: eviction
labels:
app: system
spec:
coolDownSeconds: 300
eviction:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30 #(1)
description: "evict low priority pods"
- Duration in seconds the pod needs to terminate gracefully.
apiVersion: ensurance.crane.io/v1alpha1
kind: NodeQOS
metadata:
name: "watermark3"
labels:
app: "system"
spec:
nodeQualityProbe:
timeoutSeconds: 10
nodeLocalGet:
localCacheTTLSeconds: 60
rules:
- name: "cpu-usage"
avoidanceThreshold: 2
restoreThreshold: 2
actionName: "eviction"
strategy: "Preview" #(1)
metricRule:
name: "cpu_total_usage"
value: 6000
- Strategy for the action, “Preview” to not perform actually
apiVersion: ensurance.crane.io/v1alpha1
kind: PodQOS
metadata:
name: all-elastic-pods
spec:
allowedActions:
- eviction
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
preemptible_job: "true"
Supported Metrics
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| cpu_total_usage | node cpu usage |
| cpu_total_utilization | node cpu utilization percent |
| memory_total_usage | node mem usage |
| memory_total_utilization | node mem utilization percent |
For details, please refer to the examples under examples/ensurance.
Used with dynamic resources
In order to avoid the impact of active avoidance operations on high-priority services, such as the wrongful eviction of important services, it is recommended to use PodQOS to associate workloads that use dynamic resources, so that only those workloads that use idle resources are affected when executing actions, ensuring that The stability of the core business on the node.
For the content of dymamic resources, see Dynamic resource oversold and limit.