Intelligent Autoscaling Practices Based on Effective HPA for Custom Metrics
6 minute read
The Kubernetes HPA supports rich elasticity scaling capabilities, with Kubernetes platform developers deploying services to implement custom Metric services and Kubernetes users configuring multiple built-in resource metrics or custom Metric metrics to achieve custom horizontal elasticity. Effective HPA is compatible with the community’s Kubernetes HPA capabilities, providing smarter autoscaling policies such as prediction-based autoscaling and Cron-cycle-based autoscaling. Prometheus is a popular open source monitoring system today, through which user-defined metrics configurations are accessible.
In this article, we present an example of how to implement intelligent resilience of custom metrics based on Effective HPA. Some configurations are taken from official documentation
Environment Requirements
- Kubernetes 1.18+
- Helm 3.1.0
- Crane v0.6.0+
- Prometheus
Refer to installation documentation to install Crane in the cluster, Prometheus can be used either from the installation documentation or from the deployed Prometheus.
Environment build
Installing PrometheusAdapter
The Crane components Metric-Adapter and PrometheusAdapter are both based on custom-metric-apiserver which implements When installing Crane, the corresponding ApiService will be installed as the Metric-Adapter of Crane, so you need to remove the ApiService before installing PrometheusAdapter to ensure that Helm is installed successfully.
# View the current ApiService
kubectl get apiservice
Since Crane is installed, the result is as follows.
NAME SERVICE AVAILABLE AGE
v1beta1.batch Local True 35d
v1beta1.custom.metrics.k8s.io Local True 18d
v1beta1.discovery.k8s.io Local True 35d
v1beta1.events.k8s.io Local True 35d
v1beta1.external.metrics.k8s.io crane-system/metric-adapter True 18d
v1beta1.flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io Local True 35d
v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io kube-system/metrics-service True 35d
Remove the installed ApiService by crane
kubectl delete apiservice v1beta1.external.metrics.k8s.io
Install PrometheusAdapter via Helm
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
helm install prometheus-adapter -n crane-system prometheus-community/prometheus-adapter
Then change the ApiService back to Crane’s Metric-Adapter
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gocrane/crane/main/deploy/metric-adapter/apiservice.yaml
Configure Metric-Adapter to enable RemoteAdapter functionality
The installation of PrometheusAdapter did not point the ApiService to PrometheusAdapter, so in order to allow PrometheusAdapter to provide custom Metric as well, the RemoteAdapter function of Crane Metric Adapter is used to forward requests to PrometheusAdapter.
Modify the Metric-Adapter configuration to configure PrometheusAdapter’s Service as Crane Metric Adapter’s RemoteAdapter
# View the current ApiService
kubectl edit deploy metric-adapter -n crane-system
Make the following changes based on the PrometheusAdapter configuration.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: metric-adapter
namespace: crane-system
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- args:
#Add external Adapter configuration
- --remote-adapter=true
- --remote-adapter-service-namespace=crane-system
- --remote-adapter-service-name=prometheus-adapter
- --remote-adapter-service-port=443
RemoteAdapter Capabilities
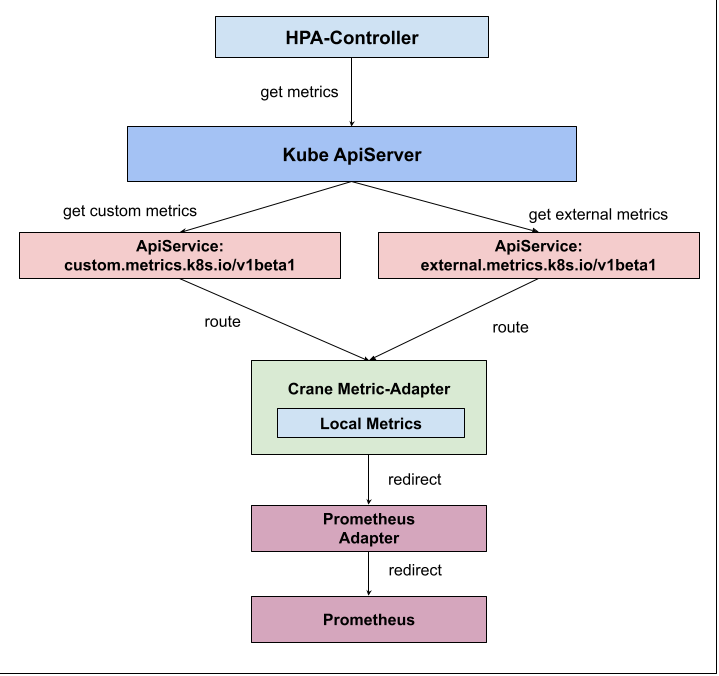
Kubernetes restricts an ApiService to configure only one backend service, so in order to use the Metric provided by Crane and the Metric provided by PrometheusAdapter within a cluster, Crane supports a RemoteAdapter to solve this problem
- Crane Metric-Adapter supports the configuration of a Kubernetes Service as a Remote Adapter
- The Crane Metric-Adapter will first check if the request is a Crane provided Local Metric, and if not, forward it to the Remote Adapter
Run the example
Preparing the application
Deploy the following application to the cluster, which exposes the Metric to show the number of http requests received per second.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: sample-app
labels:
app: sample-app
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: sample-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: sample-app
spec:
containers:
- image: luxas/autoscale-demo:v0.1.2
name: metrics-provider
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
requests:
cpu: 200m
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 8080
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: sample-app
name: sample-app
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8080
selector:
app: sample-app
type: ClusterIP
kubectl create -f sample-app.deploy.yaml
kubectl create -f sample-app.service.yaml
When the application is deployed, you can check the http_requests_total Metric with the command
curl http://$(kubectl get service sample-app -o jsonpath='{ .spec.clusterIP }')/metrics
Configure collection rules
Configure Prometheus’ ScrapeConfig to collect the application’s Metric: http_requests_total
kubectl edit configmap -n crane-system prometheus-server
Add the following configuration
- job_name: sample-app
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: default;sample-app-(.+)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_namespace
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_name
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+)
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_namespace
target_label: namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name]
action: replace
target_label: pod
At this point, you can use psql to query Prometheus: sum(rate(http_requests_total[5m])) by (pod)
Verify PrometheusAdapter
The default rule configuration of PrometheusAdapter supports converting http_requests_total to a custom metric of type Pods, verified by the command
kubectl get --raw /apis/custom.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1 | jq .
The result should include pods/http_requests:
{
"name": "pods/http_requests",
"singularName": "",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "MetricValueList",
"verbs": [
"get"
]
}
This indicates that the HPA can now be configured via Pod Metric.
Configuring autoscaling
We can now create the Effective HPA. at this point the Effective HPA can be resilient via Pod Metric http_requests:
How to define a custom metric to enable prediction
Annotation in the Effective HPA adds the configuration according to the following rules:
annotations:
# metric-query.autoscaling.crane.io is a static prefix,after that should be the Metric Type and Metric Name,It should be the same as your spec.metrics's Metric.name,Supported Metric type are Pods(pods) and External (external)
metric-query.autoscaling.crane.io/pods.http_requests: "sum(rate(http_requests_total[5m])) by (pod)"
apiVersion: autoscaling.crane.io/v1alpha1
kind: EffectiveHorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: php-apache
annotations:
# metric-query.autoscaling.crane.io 是固定的前缀,后面是 Metric 的 type 和 名字,需跟 spec.metrics 中的 Metric.name 相同,支持 Pods 类型(pods)和 External 类型(external)
metric-query.autoscaling.crane.io/pods.http_requests: "sum(rate(http_requests_total[5m])) by (pod)"
spec:
# ScaleTargetRef is the reference to the workload that should be scaled.
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: sample-app
minReplicas: 1 # MinReplicas is the lower limit replicas to the scale target which the autoscaler can scale down to.
maxReplicas: 10 # MaxReplicas is the upper limit replicas to the scale target which the autoscaler can scale up to.
scaleStrategy: Auto # ScaleStrategy indicate the strategy to scaling target, value can be "Auto" and "Manual".
# Metrics contains the specifications for which to use to calculate the desired replica count.
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 50
- type: Pods
pods:
metric:
name: http_requests
target:
type: AverageValue
averageValue: 500m
# Prediction defines configurations for predict resources.
# If unspecified, defaults don't enable prediction.
prediction:
predictionWindowSeconds: 3600 # PredictionWindowSeconds is the time window to predict metrics in the future.
predictionAlgorithm:
algorithmType: dsp
dsp:
sampleInterval: "60s"
historyLength: "7d"
kubectl create -f sample-app-hpa.yaml
Check the TimeSeriesPrediction status, which may be unpredictable if the app has been running for a short time:
apiVersion: prediction.crane.io/v1alpha1
kind: TimeSeriesPrediction
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2022-07-11T16:10:09Z"
generation: 1
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: effective-hpa-controller
app.kubernetes.io/name: ehpa-php-apache
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: php-apache
autoscaling.crane.io/effective-hpa-uid: 1322c5ac-a1c6-4c71-98d6-e85d07b22da0
name: ehpa-php-apache
namespace: default
spec:
predictionMetrics:
- algorithm:
algorithmType: dsp
dsp:
estimators: {}
historyLength: 7d
sampleInterval: 60s
resourceIdentifier: crane_pod_cpu_usage
resourceQuery: cpu
type: ResourceQuery
- algorithm:
algorithmType: dsp
dsp:
estimators: {}
historyLength: 7d
sampleInterval: 60s
expressionQuery:
expression: sum(rate(http_requests_total[5m])) by (pod)
resourceIdentifier: pods.http_requests
type: ExpressionQuery
predictionWindowSeconds: 3600
targetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: sample-app
namespace: default
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2022-07-12T06:54:42Z"
message: not all metric predicted
reason: PredictPartial
status: "False"
type: Ready
predictionMetrics:
- ready: false
resourceIdentifier: crane_pod_cpu_usage
- prediction:
- labels:
- name: pod
value: sample-app-7cfb596f98-8h5vv
samples:
- timestamp: 1657608900
value: "0.01683"
- timestamp: 1657608960
value: "0.01683"
......
ready: true
resourceIdentifier: pods.http_requests
Looking at the HPA object created by Effective HPA, you can observe that a Metric has been created based on custom metrics predictions: crane_custom.pods_http_requests.
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2022-07-11T16:10:10Z"
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: effective-hpa-controller
app.kubernetes.io/name: ehpa-php-apache
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: php-apache
autoscaling.crane.io/effective-hpa-uid: 1322c5ac-a1c6-4c71-98d6-e85d07b22da0
name: ehpa-php-apache
namespace: default
spec:
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- pods:
metric:
name: http_requests
target:
averageValue: 500m
type: AverageValue
type: Pods
- pods:
metric:
name: pods.http_requests
selector:
matchLabels:
autoscaling.crane.io/effective-hpa-uid: 1322c5ac-a1c6-4c71-98d6-e85d07b22da0
target:
averageValue: 500m
type: AverageValue
type: Pods
- resource:
name: cpu
target:
averageUtilization: 50
type: Utilization
type: Resource
minReplicas: 1
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: sample-app
Summary
Due to the complexity of production environments, multi-metric-based autoscaling (CPU/Memory/custom metrics) is often a common choice for production applications, so Effective HPA achieves the effectiveness of helping more businesses land horizontal autoscaling in production environments by covering multi-metric autoscaling with predictive algorithms.